SSR vs CSR 什么是服务端渲染?React为例理解原理
作者:神三元
part1:实现一个基础的React组件SSR 这一部分来简要实现一个React组件的SSR。
一. SSR vs CSR 什么是服务端渲染?
废话不多说,直接起一个express服务器。
app.get('/', (req, res) => {
res.send(
`
<html>
<head>
<title>hello</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>hello</h1>
<p>world</p>
</body>
</html>
`
)
})
启动之后打开localhost:3001可以看到页面显示了hello world。而且打开网页源代码:

也能够完成显示。
这就是服务端渲染。其实非常好理解,就是服务器返回一堆html字符串,然后让浏览器显示。
与服务端渲染相对的是客户端渲染(Client Side Render)。那什么是客户端渲染? 现在创建一个新的React项目,用脚手架生成项目,然后run起来。 这里你可以看到React脚手架自动生成的首页。

然而打开网页源代码。

body中除了兼容处理的noscript标签之外,只有一个id为root的标签。那首页的内容是从哪来的呢?很明显,是下面的script中拉取的JS代码控制的。
因此,CSR和SSR最大的区别在于前者的页面渲染是JS负责进行的,而后者是服务器端直接返回HTML让浏览器直接渲染。
为什么要使用服务端渲染呢?

传统CSR的弊端: 1. 由于页面显示过程要进行JS文件拉取和React代码执行,首屏加载时间会比较慢。 2. 对于SEO(Search Engine Optimazition,即搜索引擎优化),完全无能为力,因为搜索引擎爬虫只认识html结构的内容,而不能识别JS代码内容。
SSR的出现,就是为了解决这些传统CSR的弊端。
二、实现React组件的服务端渲染
刚刚起的express服务返回的只是一个普通的html字符串,但我们讨论的是如何进行React的服务端渲染,那么怎么做呢? 首先写一个简单的React组件:
// containers/Home.js
import React from 'react';
const Home = () => {
return (
<div>
<div>This is sanyuan</div>
</div>
)
}
export default Home
现在的任务就是将它转换为html代码返回给浏览器。 总所周知,JSX中的标签其实是基于虚拟DOM的,最终要通过一定的方法将其转换为真实DOM。虚拟DOM也就是JS对象,可以看出整个服务端的渲染流程就是通过虚拟DOM的编译来完成的,因此虚拟DOM巨大的表达力也可见一斑了。
而react-dom这个库中刚好实现了编译虚拟DOM的方法。做法如下:
// server/index.js
import express from 'express';
import { renderToString } from 'react-dom/server';
import Home from './containers/Home';
const app = express();
const content = renderToString(<Home />);
app.get('/', function (req, res) {
res.send(
`
<html>
<head>
<title>ssr</title>
</head>
<body>
<div id="root">${content}</div>
</body>
</html>
`
);
})
app.listen(3001, () => {
console.log('listen:3001')
})
启动express服务,再浏览器上打开对应端口,页面显示出"this is sanyuan"。 到此,就初步实现了一个React组件是服务端渲染。 当然,这只是一个非常简陋的SSR,事实上对于复杂的项目而言是无能为力的,在之后会一步步完善,打造出一个功能完整的React的SSR框架。
part2: 初识同构
一.引入同构
其实前面的SSR是不完整的,平时在开发的过程中难免会有一些事件绑定,比如加一个button:
// containers/Home.js
import React from 'react';
const Home = () => {
return (
<div>
<div>This is sanyuan</div>
<button onClick={() => {alert('666')}}>click</button>
</div>
)
}
export default Home
再试一下,你会惊奇的发现,事件绑定无效!那这是为什么呢?原因很简单,react-dom/server下的renderToString并没有做事件相关的处理,因此返回给浏览器的内容不会有事件绑定。
那怎么解决这个问题呢?
这就需要进行同构了。所谓同构,通俗的讲,就是一套React代码在服务器上运行一遍,到达浏览器又运行一遍。服务端渲染完成页面结构,浏览器端渲染完成事件绑定。
那如何进行浏览器端的事件绑定呢?
唯一的方式就是让浏览器去拉取JS文件执行,让JS代码来控制。于是服务端返回的代码变成了这样:

有没有发现和之前的区别?区别就是多了一个script标签。而它拉取的JS代码就是来完成同构的。
那么这个index.js我们如何生产出来呢?
在这里,要用到react-dom。具体做法其实就很简单了:
//client/index. js
import React from 'react';
import ReactDom from 'react-dom';
import Home from '../containers/Home';
ReactDom.hydrate(<Home />, document.getElementById('root'))
然后用webpack将其编译打包成index.js:
//webpack.client.js
const path = require('path');
const merge = require('webpack-merge');
const config = require('./webpack.base');
const clientConfig = {
mode: 'development',
entry: './src/client/index.js',
output: {
filename: 'index.js',
path: path.resolve(__dirname, 'public')
},
}
module.exports = merge(config, clientConfig);
//webpack.base.js
module.exports = {
module: {
rules: [{
test: /\.js$/,
loader: 'babel-loader',
exclude: /node_modules/,
options: {
presets: ['@babel/preset-react', ['@babel/preset-env', {
targets: {
browsers: ['last 2 versions']
}
}]]
}
}]
}
}
//package.json的script部分
"scripts": {
"dev": "npm-run-all --parallel dev:**",
"dev:start": "nodemon --watch build --exec node \"./build/bundle.js\"",
"dev:build:server": "webpack --config webpack.server.js --watch",
"dev:build:client": "webpack --config webpack.client.js --watch"
},
在这里需要开启express的静态文件服务:
const app = express();
app.use(express.static('public'));
现在前端的script就能拿到控制浏览器的JS代码啦。
绑定事件完成!
现在来初步总结一下同构代码执行的流程:

二.同构中的路由问题
现在写一个路由的配置文件:
// Routes.js
import React from 'react';
import {Route} from 'react-router-dom'
import Home from './containers/Home';
import Login from './containers/Login'
export default (
<div>
<Route path='/' exact component={Home}></Route>
<Route path='/login' exact component={Login}></Route>
</div>
)
在客户端的控制代码,也就是上面写过的client/index.js中,要做相应的更改:
import React from 'react';
import ReactDom from 'react-dom';
import { BrowserRouter } from 'react-router-dom'
import Routes from '../Routes'
const App = () => {
return (
<BrowserRouter>
{Routes}
</BrowserRouter>
)
}
ReactDom.hydrate(<App />, document.getElementById('root'))
这时候控制台会报错,

因为在Routes.js中,每个Route组件外面包裹着一层div,但服务端返回的代码中并没有这个div,所以报错。如何去解决这个问题?需要将服务端的路由逻辑执行一遍。
// server/index.js
import express from 'express';
import {render} from './utils';
const app = express();
app.use(express.static('public'));
//注意这里要换成*来匹配
app.get('*', function (req, res) {
res.send(render(req));
});
app.listen(3001, () => {
console.log('listen:3001')
});
// server/utils.js
import Routes from '../Routes'
import { renderToString } from 'react-dom/server';
//重要是要用到StaticRouter
import { StaticRouter } from 'react-router-dom';
import React from 'react'
export const render = (req) => {
//构建服务端的路由
const content = renderToString(
<StaticRouter location={req.path} >
{Routes}
</StaticRouter>
);
return `
<html>
<head>
<title>ssr</title>
</head>
<body>
<div id="root">${content}</div>
<script src="/index.js"></script>
</body>
</html>
`
}
现在路由的跳转就没有任何问题啦。 注意,这里仅仅是一级路由的跳转,多级路由的渲染在之后的系列中会用react-router-config中renderRoutes来处理。
part3: 同构项目中引入Redux
这一节主要是讲述Redux如何被引入到同构项目中以及其中需要注意的问题。
重新回顾一下redux的运作流程:

再回顾一下同构的概念,即在React代码客户端和服务器端各自运行一遍。
一、创建全局store
现在开始创建store。 在项目根目录的store文件夹(总的store)下:
import {createStore, applyMiddleware, combineReducers} from 'redux';
import thunk from 'redux-thunk';
import { reducer as homeReducer } from '../containers/Home/store';
//合并项目组件中store的reducer
const reducer = combineReducers({
home: homeReducer
})
//创建store,并引入中间件thunk进行异步操作的管理
const store = createStore(reducer, applyMiddleware(thunk));
//导出创建的store
export default store
二、组件内action和reducer的构建
Home文件夹下的工程文件结构如下:

在Home的store目录下的各个文件代码示例:
//constants.js
export const CHANGE_LIST = 'HOME/CHANGE_LIST';
//actions.js
import axios from 'axios';
import { CHANGE_LIST } from "./constants";
//普通action
const changeList = list => ({
type: CHANGE_LIST,
list
});
//异步操作的action(采用thunk中间件)
export const getHomeList = () => {
return (dispatch) => {
return axios.get('xxx')
.then((res) => {
const list = res.data.data;
console.log(list)
dispatch(changeList(list))
});
};
}
//reducer.js
import { CHANGE_LIST } from "./constants";
const defaultState = {
name: 'sanyuan',
list: []
}
export default (state = defaultState, action) => {
switch(action.type) {
default:
return state;
}
}
//index.js
import reducer from "./reducer";
//这么做是为了导出reducer让全局的store来进行合并
//那么在全局的store下的index.js中只需引入Home/store而不需要Home/store/reducer.js
//因为脚手架会自动识别文件夹下的index文件
export {reducer}
三、组件连接全局store
下面是Home组件的编写示例。
import React, { Component } from 'react';
import { connect } from 'react-redux';
import { getHomeList } from './store/actions'
class Home extends Component {
render() {
const { list } = this.props
return list.map(item => <div key={item.id}>{item.title}</div>)
}
}
const mapStateToProps = state => ({
list: state.home.newsList,
})
const mapDispatchToProps = dispatch => ({
getHomeList() {
dispatch(getHomeList());
}
})
//连接store
export default connect(mapStateToProps, mapDispatchToProps)(Home);对于store的连接操作,在同构项目中分两个部分,一个是与客户端store的连接,另一部分是与服务端store的连接。都是通过react-redux中的Provider来传递store的。
客户端:
//src/client/index.js
import React from 'react';
import ReactDom from 'react-dom';
import {BrowserRouter, Route} from 'react-router-dom';
import { Provider } from 'react-redux';
import store from '../store'
import routes from '../routes.js'
const App = () => {
return (
<Provider store={store}>
<BrowserRouter>
{routes}
</BrowserRouter>
</Provider>
)
}
ReactDom.hydrate(<App />, document.getElementById('root'))
服务端:
//src/server/index.js的内容保持不变
//下面是src/server/utils.js
import Routes from '../Routes'
import { renderToString } from 'react-dom/server';
import { StaticRouter } from 'react-router-dom';
import { Provider } from 'react-redux';
import React from 'react'
export const render = (req) => {
const content = renderToString(
<Provider store={store}>
<StaticRouter location={req.path} >
{Routes}
</StaticRouter>
</Provider>
);
return `
<html>
<head>
<title>ssr</title>
</head>
<body>
<div id="root">${content}</div>
<script src="/index.js"></script>
</body>
</html>
`
}
四、潜在的坑
其实上面这样的store创建方式是存在问题的,什么原因呢?
上面的store是一个单例,当这个单例导出去后,所有的用户用的是同一份store,这是不应该的。那么这么解这个问题呢?
在全局的store/index.js下修改如下:
//导出部分修改
export default () => {
return createStore(reducer, applyMiddleware(thunk))
}
这样在客户端和服务端的js文件引入时其实引入了一个函数,把这个函数执行就会拿到一个新的store,这样就能保证每个用户访问时都是用的一份新的store。
part4: 异步数据的服务端渲染方案(数据注水与脱水)
一、问题引入
在平常客户端的React开发中,我们一般在组件的componentDidMount生命周期函数进行异步数据的获取。但是,在服务端渲染中却出现了问题。
现在我在componentDidMount钩子函数中进行Ajax请求:
import { getHomeList } from './store/actions'
//......
componentDidMount() {
this.props.getList();
}
//......
const mapDispatchToProps = dispatch => ({
getList() {
dispatch(getHomeList());
}
})
//actions.js
import { CHANGE_LIST } from "./constants";
import axios from 'axios'
const changeList = list => ({
type: CHANGE_LIST,
list
})
export const getHomeList = () => {
return dispatch => {
//另外起的本地的后端服务
return axiosInstance.get('localhost:4000/api/news.json')
.then((res) => {
const list = res.data.data;
dispatch(changeList(list))
})
}
}
//reducer.js
import { CHANGE_LIST } from "./constants";
const defaultState = {
name: 'sanyuan',
list: []
}
export default (state = defaultState, action) => {
switch(action.type) {
case CHANGE_LIST:
const newState = {
...state,
list: action.list
}
return newState
default:
return state;
}
}
好,现在启动服务。

现在页面能够正常渲染,但是打开网页源代码。

源代码里面并没有这些列表数据啊!那这是为什么呢?
让我们来分析一下客户端和服务端的运行流程,当浏览器发送请求时,服务器接受到请求,这时候服务器和客户端的store都是空的,紧接着客户端执行componentDidMount生命周期中的函数,获取到数据并渲染到页面,然而服务器端始终不会执行componentDidMount,因此不会拿到数据,这也导致服务器端的store始终是空的。换而言之,关于异步数据的操作始终只是客户端渲染。
现在的工作就是让服务端将获得数据的操作执行一遍,以达到真正的服务端渲染的效果。
二、改造路由
在完成这个方案之前需要改造一下原有的路由,也就是routes.js
import Home from './containers/Home';
import Login from './containers/Login';
export default [
{
path: "/",
component: Home,
exact: true,
loadData: Home.loadData,//服务端获取异步数据的函数
key: 'home'
},
{
path: '/login',
component: Login,
exact: true,
key: 'login'
}
}];
此时客户端和服务端中编写的JSX代码也发生了相应变化
//客户端
//以下的routes变量均指routes.js导出的数组
<Provider store={store}>
<BrowserRouter>
<div>
{
routers.map(route => {
<Route {...route} />
})
}
</div>
</BrowserRouter>
</Provider>
//服务端
<Provider store={store}>
<StaticRouter>
<div>
{
routers.map(route => {
<Route {...route} />
})
}
</div>
</StaticRouter>
</Provider>
其中配置了一个loadData参数,这个参数代表了服务端获取数据的函数。每次渲染一个组件获取异步数据时,都会调用相应组件的这个函数。因此,在编写这个函数具体的代码之前,我们有必要想清楚如何来针对不同的路由来匹配不同的loadData函数。
在server/utils.js中加入以下逻辑
import { matchRoutes } from 'react-router-config';
//调用matchRoutes用来匹配当前路由(支持多级路由)
const matchedRoutes = matchRoutes(routes, req.path)
//promise对象数组
const promises = [];
matchedRoutes.forEach(item => {
//如果这个路由对应的组件有loadData方法
if (item.route.loadData) {
//那么就执行一次,并将store传进去
//注意loadData函数调用后需要返回Promise对象
promises.push(item.route.loadData(store))
}
})
Promise.all(promises).then(() => {
//此时该有的数据都已经到store里面去了
//执行渲染的过程(res.send操作)
}
)
现在就可以安心的写我们的loadData函数,其实前面的铺垫工作做好后,这个函数是相当容易的。
import { getHomeList } from './store/actions'
Home.loadData = (store) => {
return store.dispatch(getHomeList())
}
//actions.js
export const getHomeList = () => {
return dispatch => {
return axios.get('xxxx')
.then((res) => {
const list = res.data.data;
dispatch(changeList(list))
})
}
}
根据这个思路,服务端渲染中异步数据的获取功能就完成啦。
三、数据的注水和脱水
其实目前做了这里还是存在一些细节问题的。比如当我将生命周期钩子里面的异步请求函数注释,现在页面中不会有任何的数据,但是打开网页源代码,却发现:
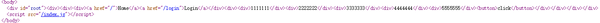
数据已经挂载到了服务端返回的HTML代码中。那这就说明服务端和客户端的store不同步的问题。
其实也很好理解。当服务端拿到store并获取数据后,客户端的js代码又执行一遍,在客户端代码执行的时候又创建了一个空的store,两个store的数据不能同步。
那如何才能让这两个store的数据同步变化呢?
首先,在服务端获取获取之后,在返回的html代码中加入这样一个script标签:
<script>
window.context = {
state: ${JSON.stringify(store.getState())}
}
</script>这叫做数据的“注水”操作,即把服务端的store数据注入到window全局环境中。 接下来是“脱水”处理,换句话说也就是把window上绑定的数据给到客户端的store,可以在客户端store产生的源头进行,即在全局的store/index.js中进行。
//store/index.js
import {createStore, applyMiddleware, combineReducers} from 'redux';
import thunk from 'redux-thunk';
import { reducer as homeReducer } from '../containers/Home/store';
const reducer = combineReducers({
home: homeReducer
})
//服务端的store创建函数
export const getStore = () => {
return createStore(reducer, applyMiddleware(thunk));
}
//客户端的store创建函数
export const getClientStore = () => {
const defaultState = window.context ? window.context.state : {};
return createStore(reducer, defaultState, applyMiddleware(thunk));
}
至此,数据的脱水和注水操作完成。但是还是有一些瑕疵,其实当服务端获取数据之后,客户端并不需要再发送Ajax请求了,而客户端的React代码仍然存在这样的浪费性能的代码。怎么办呢?
还是在Home组件中,做如下的修改:
componentDidMount() {
//判断当前的数据是否已经从服务端获取
//要知道,如果是首次渲染的时候就渲染了这个组件,则不会重复发请求
//若首次渲染页面的时候未将这个组件渲染出来,则一定要执行异步请求的代码
//这两种情况对于同一组件是都是有可能发生的
if (!this.props.list.length) {
this.props.getHomeList()
}
}
一路做下来,异步数据的服务端渲染还是比较复杂的,但是难度并不是很大,需要耐心地理清思路。
至此一个比较完整的SSR框架就搭建的差不多了,但是还有一些内容需要补充,之后会继续更新的。加油吧!
part5: node作中间层及请求代码优化
一、为什么要引入node中间层?
其实任何技术都是与它的应用场景息息相关的。这里我们反复谈的SSR,其实不到万不得已我们是用不着它的,SSR所解决的最大的痛点在于SEO,但它同时带来了更昂贵的成本。不仅因为服务端渲染需要更加复杂的处理逻辑,还因为同构的过程需要服务端和客户端都执行一遍代码,这虽然对于客户端并没有什么大碍,但对于服务端却是巨大的压力,因为数量庞大的访问量,对于每一次访问都要另外在服务器端执行一遍代码进行计算和编译,大大地消耗了服务器端的性能,成本随之增加。如果访问量足够大的时候,以前不用SSR的时候一台服务器能够承受的压力现在或许要增加到10台才能抗住。痛点在于SEO,但如果实际上对SEO要求并不高的时候,那使用SSR就大可不必了。
那同样地,为什么要引入node作为中间层呢?它是处在哪两者的中间?又是解决了什么场景下的问题?
在不用中间层的前后端分离开发模式下,前端一般直接请求后端的接口。但真实场景下,后端所给的数据格式并不是前端想要的,但处于性能原因或者其他的因素接口格式不能更改,这时候需要在前端做一些额外的数据处理操作。前端来操作数据本身无可厚非,但是当数据量变得庞大起来,那么在客户端就是产生巨大的性能损耗,甚至影响到用户体验。在这个时候,node中间层的概念便应运而生。
它最终解决的前后端协作的问题。
一般的中间层工作流是这样的:前端每次发送请求都是去请求node层的接口,然后node对于相应的前端请求做转发,用node去请求真正的后端接口获取数据,获取后再由node层做对应的数据计算等处理操作,然后返回给前端。这就相当于让node层替前端接管了对数据的操作。

二、SSR框架中引入中间层
在之前搭建的SSR框架中,服务端和客户端请求利用的是同一套请求后端接口的代码,但这是不科学的。
对客户端而言,最好通过node中间层。而对于这个SSR项目而言,node开启的服务器本来就是一个中间层的角色,因而对于服务器端执行数据请求而言,就可以直接请求真正的后端接口啦。
//actions.js
//参数server表示当前请求是否发生在node服务端
const getUrl = (server) => {
return server ? 'xxxx(后端接口地址)' : '/api/sanyuan.json(node接口)';
}
//这个server参数是Home组件里面传过来的,
//在componentDidMount中调用这个action时传入false,
//在loadData函数中调用时传入true, 这里就不贴组件代码了
export const getHomeList = (server) => {
return dispatch => {
return axios.get(getUrl(server))
.then((res) => {
const list = res.data.data;
dispatch(changeList(list))
})
}
}
在server/index.js应拿到前端的请求做转发,这里是直接用proxy形式来做,也可以用node单独向后端发送一次HTTP请求。
//增加如下代码
import proxy from 'express-http-proxy';
//相当于拦截到了前端请求地址中的/api部分,然后换成另一个地址
app.use('/api', proxy('http://xxxxxx(服务端地址)', {
proxyReqPathResolver: function(req) {
return '/api'+req.url;
}
}));
三、请求代码优化
其实请求的代码还是有优化的余地的,仔细想想,上面的server参数其实是不用传递的。
现在我们利用axios的instance和thunk里面的withExtraArgument来做一些封装。
//新建server/request.js
import axios from 'axios'
const instance = axios.create({
baseURL: 'http://xxxxxx(服务端地址)'
})
export default instance
//新建client/request.js
import axios from 'axios'
const instance = axios.create({
//即当前路径的node服务
baseURL: '/'
})
export default instance
然后对全局下store的代码做一个微调:
import {createStore, applyMiddleware, combineReducers} from 'redux';
import thunk from 'redux-thunk';
import { reducer as homeReducer } from '../containers/Home/store';
import clientAxios from '../client/request';
import serverAxios from '../server/request';
const reducer = combineReducers({
home: homeReducer
})
export const getStore = () => {
//让thunk中间件带上serverAxios
return createStore(reducer, applyMiddleware(thunk.withExtraArgument(serverAxios)));
}
export const getClientStore = () => {
const defaultState = window.context ? window.context.state : {};
//让thunk中间件带上clientAxios
return createStore(reducer, defaultState, applyMiddleware(thunk.withExtraArgument(clientAxios)));
}
现在Home组件中请求数据的action无需传参,actions.js中的请求代码如下:
export const getHomeList = () => {
//返回函数中的默认第三个参数是withExtraArgument传进来的axios实例
return (dispatch, getState, axiosInstance) => {
return axiosInstance.get('/api/sanyuan.json')
.then((res) => {
const list = res.data.data;
console.log(res)
dispatch(changeList(list))
})
}
}
至此,代码优化就做的差不多了,这种代码封装的技巧其实可以用在其他的项目当中,其实还是比较优雅的。
part6: 多级路由渲染(renderRoutes)
现在将routes.js的内容改变如下:
import Home from './containers/Home';
import Login from './containers/Login';
import App from './App'
//这里出现了多级路由
export default [{
path: '/',
component: App,
routes: [
{
path: "/",
component: Home,
exact: true,
loadData: Home.loadData,
key: 'home',
},
{
path: '/login',
component: Login,
exact: true,
key: 'login',
}
]
}]
现在的需求是让页面公用一个Header组件,App组件编写如下:
import React from 'react';
import Header from './components/Header';
const App = (props) => {
console.log(props.route)
return (
<div>
<Header></Header>
</div>
)
}
export default App;
对于多级路由的渲染,需要服务端和客户端各执行一次。 因此编写的JSX代码都应有所实现:
//routes是指routes.js中返回的数组
//服务端:
<Provider store={store}>
<StaticRouter location={req.path} >
<div>
{renderRoutes(routes)}
</div>
</StaticRouter>
</Provider>
//客户端:
<Provider store={getClientStore()}>
<BrowserRouter>
<div>
{renderRoutes(routes)}
</div>
</BrowserRouter>
</Provider>
这里都用到了renderRoutes方法,其实它的工作非常简单,就是根据url渲染一层路由的组件(这里渲染的是App组件),然后将下一层的路由通过props传给目前的App组件,依次循环。
那么,在App组件就能通过props.route.routes拿到下一层路由进行渲染:
import React from 'react';
import Header from './components/Header';
//增加renderRoutes方法
import { renderRoutes } from 'react-router-config';
const App = (props) => {
console.log(props.route)
return (
<div>
<Header></Header>
<!--拿到Login和Home组件的路由-->
{renderRoutes(props.route.routes)}
</div>
)
}
export default App;
至此,多级路由的渲染就完成啦。
part7: CSS的服务端渲染思路(context钩子变量)
一、客户端项目中引入CSS
还是以Home组件为例
//Home/style.css
body {
background: gray;
}
现在,在Home组件代码中引入:
import styles from './style.css';
要知道这样的引入CSS代码的方式在一般环境下是运行不起来的,需要在webpack中做相应的配置。 首先安装相应的插件。
npm install style-loader css-loader --D
//webpack.client.js
const path = require('path');
const merge = require('webpack-merge');
const config = require('./webpack.base');
const clientConfig = {
mode: 'development',
entry: './src/client/index.js',
module: {
rules: [{
test: /\.css?$/,
use: ['style-loader', {
loader: 'css-loader',
options: {
modules: true
}
}]
}]
},
output: {
filename: 'index.js',
path: path.resolve(__dirname, 'public')
},
}
module.exports = merge(config, clientConfig);
//webpack.base.js代码,回顾一下,配置了ES语法相关的内容
module.exports = {
module: {
rules: [{
test: /\.js$/,
loader: 'babel-loader',
exclude: /node_modules/,
options: {
presets: ['@babel/preset-react', ['@babel/preset-env', {
targets: {
browsers: ['last 2 versions']
}
}]]
}
}]
}
}
好,现在在客户端CSS已经产生了效果。

可是打开网页源代码:

咦?里面并没有出现任何有关CSS样式的代码啊!那这是什么原因呢?很简单,其实我们的服务端的CSS加载还没有做。接下来我们来完成CSS代码的服务端的处理。
二、服务端CSS的引入
首先,来安装一个webpack的插件,
npm install -D isomorphic-style-loader
然后再webpack.server.js中做好相应的css配置:
//webpack.server.js
const path = require('path');
const nodeExternals = require('webpack-node-externals');
const merge = require('webpack-merge');
const config = require('./webpack.base');
const serverConfig = {
target: 'node',
mode: 'development',
entry: './src/server/index.js',
externals: [nodeExternals()],
module: {
rules: [{
test: /\.css?$/,
use: ['isomorphic-style-loader', {
loader: 'css-loader',
options: {
modules: true
}
}]
}]
},
output: {
filename: 'bundle.js',
path: path.resolve(__dirname, 'build')
}
}
module.exports = merge(config, serverConfig);
它做了些什么事情?
再看看这行代码:
import styles from './style.css';
引入css文件时,这个isomorphic-style-loader帮我们在styles中挂了三个函数。输出styles看看:

现在我们的目标是拿到CSS代码,直接通过styles._getCss即可获得。
那我们拿到CSS代码后放到哪里呢?其实react-router-dom中的StaticRouter中已经帮我们准备了一个钩子变量context。如下
//context从外界传入
<StaticRouter location={req.path} context={context}>
<div>
{renderRoutes(routes)}
</div>
</StaticRouter>
这就意味着在路由配置对象routes中的组件都能在服务端渲染的过程中拿到这个context,而且这个context对于组件来说,就相当于组件中的props.staticContext。并且,这个props.staticContext只会在服务端渲染的过程中存在,而客户端渲染的时候不会被定义。这就让我们能够通过这个变量来区分两种渲染环境啦。
现在,我们需要在服务端的render函数执行之前,初始化context变量的值:
let context = { css: [] }
我们只需要在组件的componentWillMount生命周期中编写相应的逻辑即可:
componentWillMount() {
//判断是否为服务端渲染环境
if (this.props.staticContext) {
this.props.staticContext.css.push(styles._getCss())
}
}
服务端的renderToString执行完成后,context的CSS现在已经是一个有内容的数组,让我们来获取其中的CSS代码:
//拼接代码
const cssStr = context.css.length ? context.css.join('\n') : '';
现在挂载到页面:
//放到返回的html字符串里的header里面
<style>${cssStr}</style>

网页源代码中看到了CSS代码,效果也没有问题。CSS渲染完成!
三、利用高阶组件优化代码
也许你已经发现,对于每一个含有样式的组件,都需要在componentWillMount生命周期中执行完全相同的逻辑,对于这些逻辑我们是否能够把它封装起来,不用反复出现呢?
其实是可以实现的。利用高阶组件就可以完成:
//根目录下创建withStyle.js文件
import React, { Component } from 'react';
//函数返回组件
//需要传入的第一个参数是需要装饰的组件
//第二个参数是styles对象
export default (DecoratedComponent, styles) => {
return class NewComponent extends Component {
componentWillMount() {
//判断是否为服务端渲染过程
if (this.props.staticContext) {
this.props.staticContext.css.push(styles._getCss())
}
}
render() {
return <DecoratedComponent {...this.props} />
}
}
}然后让这个导出的函数包裹我们的Home组件。
import WithStyle from '../../withStyle';
//......
const exportHome = connect(mapStateToProps, mapDispatchToProps)(withStyle(Home, styles));
export default exportHome;
这样是不是简洁很多了呢?将来对于越来越多的组件,采用这种方式也是完全可以的。
part8: 做好SEO的一些技巧,引入react-helmet
这一节我们来简单的聊一点SEO相关的内容。
一、SEO技巧分享
所谓SEO(Search Engine Optimization),指的是利用搜索引擎的规则提高网站在有关搜索引擎内的自然排名。现在的搜索引擎爬虫一般是全文分析的模式,分析内容涵盖了一个网站主要3个部分的内容:文本、多媒体(主要是图片)和外部链接,通过这些来判断网站的类型和主题。因此,在做SEO优化的时候,可以围绕这三个角度来展开。
对于文本来说,尽量不要抄袭已经存在的文章,以写技术博客为例,东拼西凑抄来的文章排名一般不会高,如果需要引用别人的文章要记得声明出处,不过最好是原创,这样排名效果会比较好。多媒体包含了视频、图片等文件形式,现在比较权威的搜索引擎爬虫比如Google做到对图片的分析是基本没有问题的,因此高质量的图片也是加分项。另外是外部链接,也就是网站中a标签的指向,最好也是和当前网站相关的一些链接,更容易让爬虫分析。
当然,做好网站的门面,也就是标题和描述也是至关重要的。如:

网站标题中不仅仅包含了关键词,而且有比较详细和靠谱的描述,这让用户一看到就觉得非常亲切和可靠,有一种想要点击的冲动,这就表明网站的转化率比较高。
二、引入react-helmet
而React项目中,开发的是单页面的应用,页面始终只有一份title和description,如何根据不同的组件显示来对应不同的网站标题和描述呢?
其实是可以做到的。
npm install react-helmet --save
组件代码:(还是以Home组件为例)
import { Helmet } from 'react-helmet';
//...
render() {
return (
<Fragment>
<!--Helmet标签中的内容会被放到客户端的head部分-->
<Helmet>
<title>这是三元的技术博客,分享前端知识</title>
<meta name="description" content="这是三元的技术博客,分享前端知识"/>
</Helmet>
<div className="test">
{
this.getList()
}
</div>
</Fragment>
);
//...
这只是做了客户端的部分,在服务端仍需要做相应的处理。
其实也非常简单:
//server/utils.js
import { renderToString } from 'react-dom/server';
import { StaticRouter } from 'react-router-dom';
import React from 'react';
import { Provider } from "react-redux";
import { renderRoutes } from 'react-router-config';
import { Helmet } from 'react-helmet';
export const render = (store, routes, req, context) => {
const content = renderToString(
<Provider store={store}>
<StaticRouter location={req.path} context={context}>
<div>
{renderRoutes(routes)}
</div>
</StaticRouter>
</Provider>
);
//拿到helmet对象,然后在html字符串中引入
const helmet = Helmet.renderStatic();
const cssStr = context.css.length ? context.css.join('\n') : '';
return `
<html>
<head>
<style>${cssStr}</style>
${helmet.title.toString()}
${helmet.meta.toString()}
</head>
<body>
<div id="root">${content}</div>
<script>
window.context = {
state: ${JSON.stringify(store.getState())}
}
</script>
<script src="/index.js"></script>
</body>
</html>
`
};
现在来看看效果:

网页源代码中显示出对应的title和description, 客户端的显示也没有任何问题,大功告成!
关于React的服务端渲染原理,就先分享到这里,内容还是比较复杂的,对于前端的综合能力要求也比较高,但是坚持跟着学下来,一定会大有裨益的。






